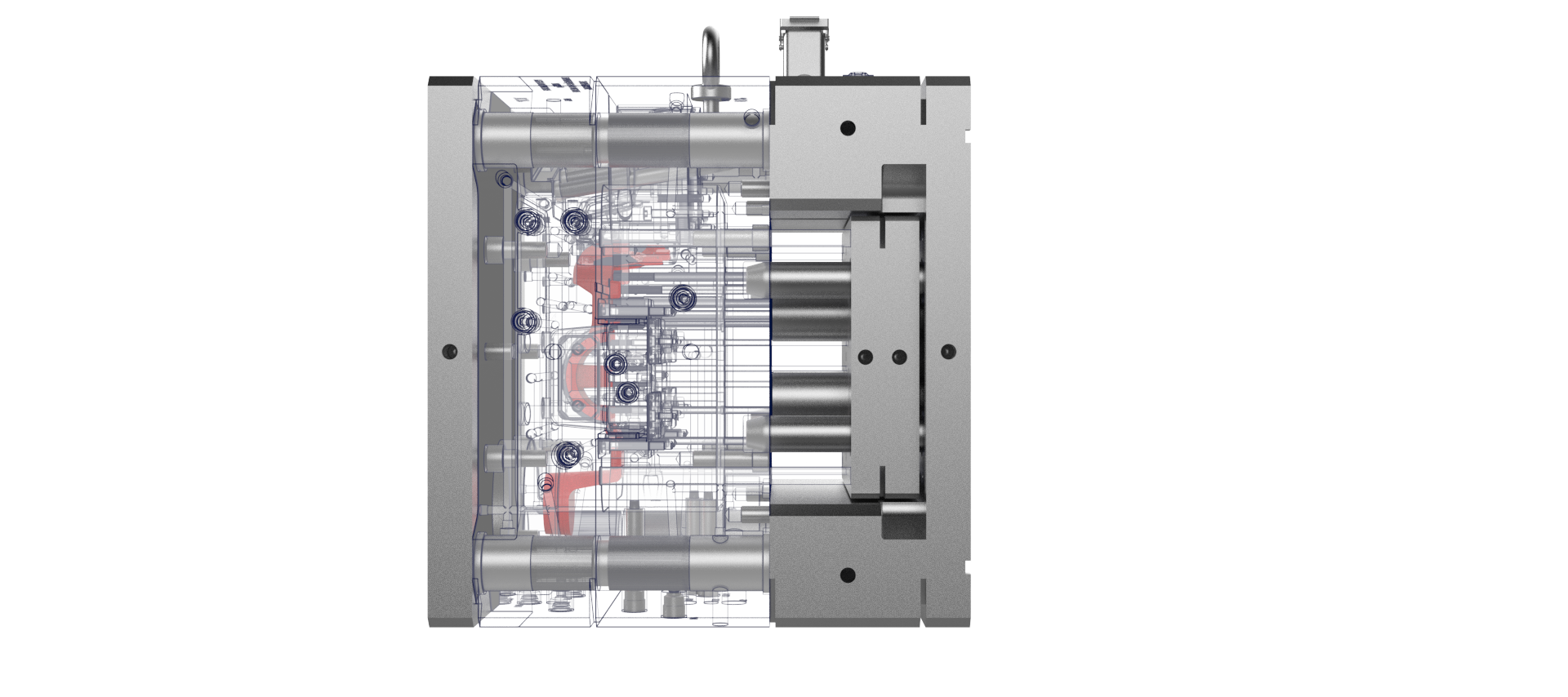
The role of prototypes in design validation
Prototypes play a key role in product development, allowing a design to be evaluated and refined prior to final production. These preliminary models not only help to define the geometry, functionality and aesthetics of a part, but also minimise risk and optimise resources.
In this article, we explore why the prototyping phase is crucial in the design process.
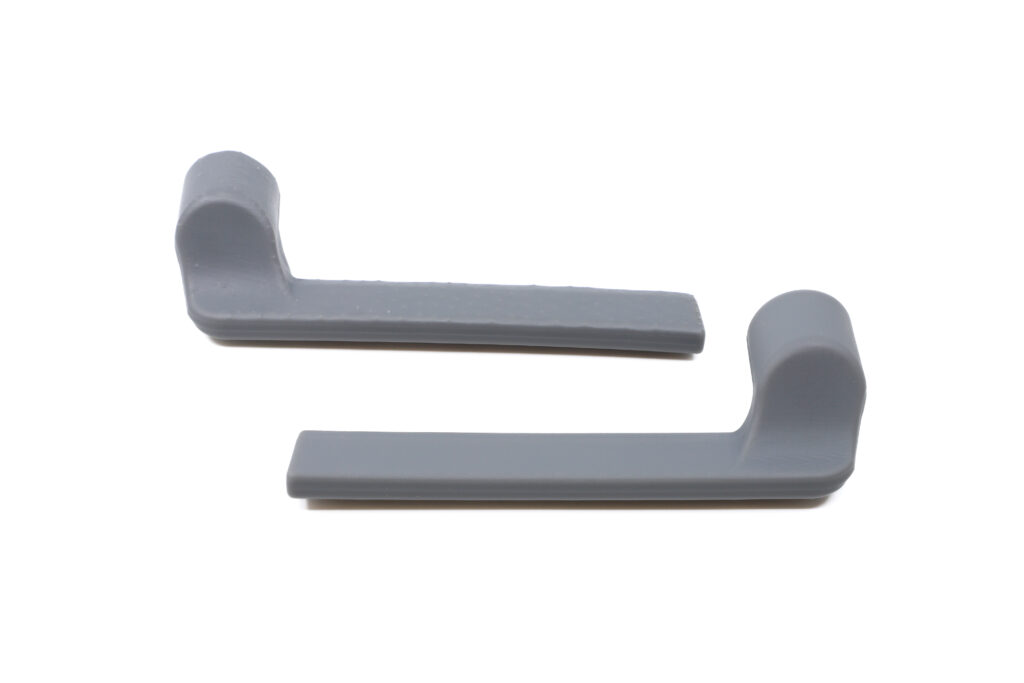

What is a prototype?
In industrial design, a prototype is a preliminary representation of a part used to evaluate different aspects of the design, such as:
- Form
- Dimension
- Aesthetics
- Functionality
Key prototyping techniques
3D printing
3D printing is a fast and cost-effective method of obtaining dimensionally accurate models to evaluate visual aspects and verify the assembly with other components. It can be used to identify gaps, dimensional errors, ergonomic problems or to compare different versions of a design before making a final decision.
However, its main limitation is the materials available. Although it can approximate the real behaviour of the part, it does not always faithfully reproduce its mechanical properties, making it difficult to evaluate parameters such as strength or durability.
Laser cutting
Laser cutting is a rapid prototyping technique that can produce accurate parts in a wide range of materials. It is very useful for prototyping parts that are to be industrialised by pressing processes.
This process is ideal for accurately checking the dimensions and functionality of parts. However, it has limitations in terms of material thickness and can only be used for flat shapes, which limits its application to complex geometries.
CNC machining
CNC machining is ideal for metal prototypes, as it provides an accurate representation of the final part, both aesthetically and functionally. Although this process is more costly and time consuming, it is essential for validating complex geometries and testing the mechanical properties of the part.
CNC prototypes allow functional testing, identification of potential failure zones and geometry adjustments to optimise part performance.
Mixed prototyping
Sometimes design projects involve the improvement of an existing part. In this case, mixed prototyping uses different techniques (such as cutting, drilling or machining) to physically modify a prototype and verify the changes made. This approach is particularly useful in the early stages of design, when parts are not yet fully defined.
Advantages of prototyping
The development of prototypes offers key advantages in the design process, allowing various aspects to be validated before moving on to the industrialisation phase:
- Aesthetics: Aesthetic aspects such as surface imperfections or small defects that are difficult to detect in 3D models can be improved.
- Dimension: Having the physical part makes it possible to verify aspects such as ergonomics or the dimensional coherence of the part in relation to the other elements.
- Fitting: It is essential that all the parts fit together correctly. Prototypes allow physical assemblies to be made to identify and correct fit errors, avoiding costly modifications to interrelated parts.
- Technical requirements: Prototyping allows parts to be tested to ensure they meet aspects such as stiffness, flexibility, strength, torsion, cycles life or corrosion resistance, among others.
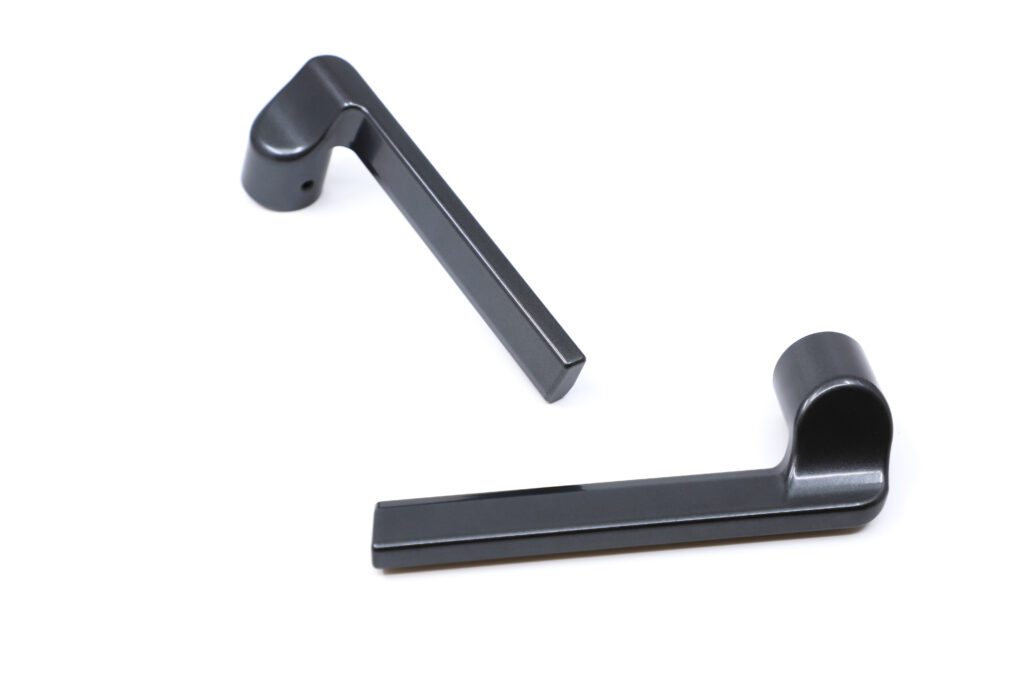

At STAC Industry, prototypes are essential to all design processes. They allow us to obtain physical parts prior to production, making it easier to identify errors and implement improvements. This saves a lot of time and money, avoids costly corrections and ensures that the final product meets the established technical and aesthetic requirements.
Contact us
We’ll be happy to provide help for your projects and resolve any doubts as soon as possible